Innovation and R&D
Technology
Innovation
TLS Logistics follows its flexible and value-added approach to customers in Research & Development, and Innovation. Innovation and R&D activities at TLS are carried out with multidisciplinary human resources that emphasize flexibility, creativity, analysis, strategic planning, collaboration, quality, and continuous improvement. TLS develops and implements many projects under the umbrella of the disruptive technological revolution Industry 4.0 - Logistics 4.0.
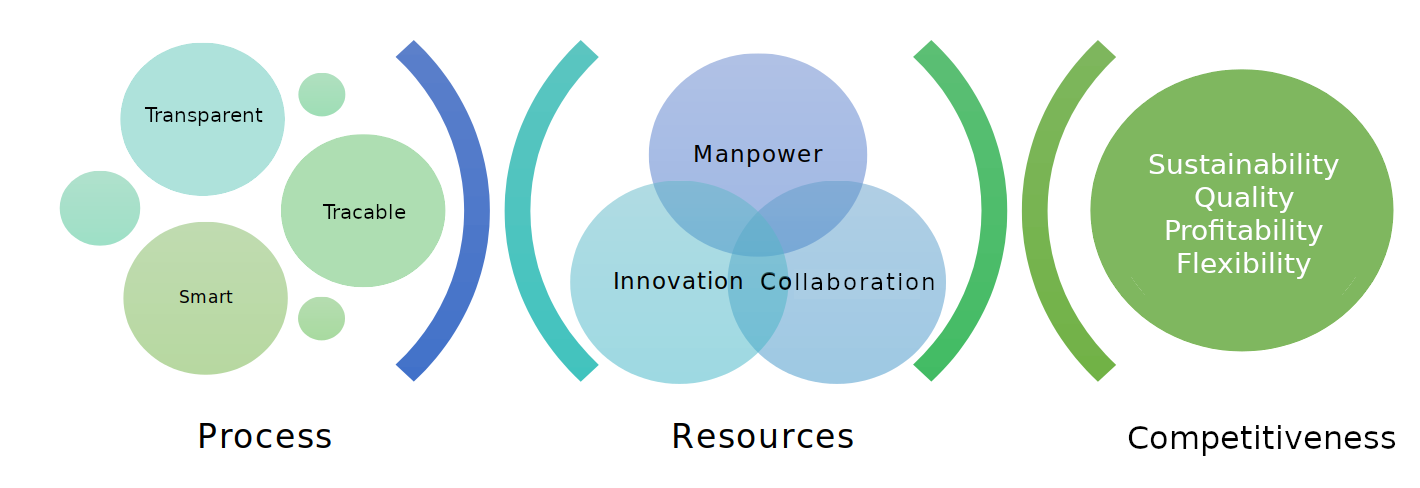
TLS Logistics’ R&D vision is to provide transparent, traceable, and intelligent logistics operations that give customers a competitive advantage. In this context, creative innovation projects are being developed to prepare hardware and software infrastructures that enable transparent access to data; traceable information screens that enable the analysis and comparison of Big Data stored in the systems, data analysis, optimization, and advanced predictive algorithms intelligent decision-making mechanisms.
TLS R&D and Innovation Processes
R&D processes begin with the development of an idea to fill a need. This idea is evaluated for its feasibility and viability. The technical problem is solved by creating a conceptual design and performing simulations. The idea is transformed into a product prototype by making improvements to the simulations. The prototype is tested under real conditions and compared with simulations, and the changes are monitored. As needed, advances are made, and the intended results are achieved. Products can be physical, software, processes, or methods.
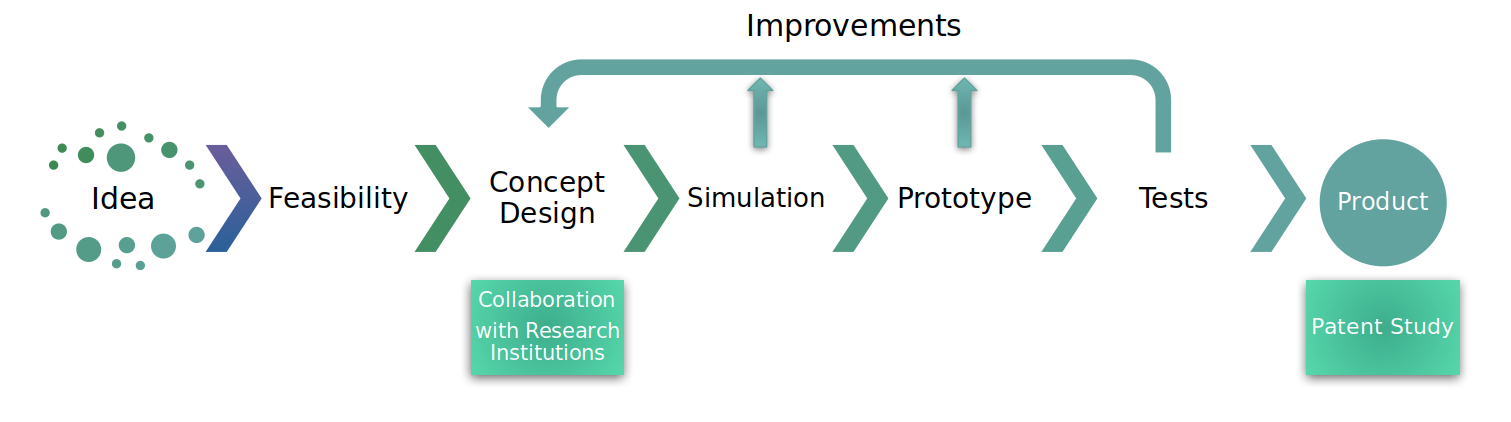
Project Management
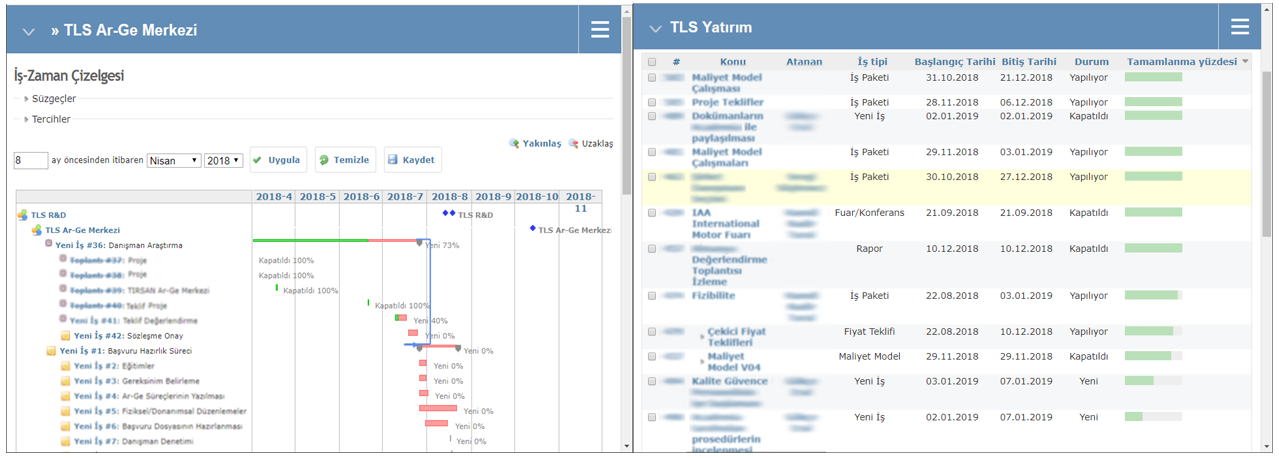
At TLS Logistics, R&D and innovation projects are planned in detail and managed through the TLS project management portal. Project management is done using current industry standards and efficient, agile methodologies. Optimization of resources used to complete work packages and indicators of project results (cost, time, and scope) are constantly monitored.
TLS R&D Center Management Strategy
Strategic planning
- Future Vision
- Situation Analysis (SWOT / PEST)
- Open Innovation
- Sustainable R&D Goals
- Technological Pioneer
Operational Excellence
- Operational Analysis
- Lean Studies
- 6 Sigma and 5S applications
- Customer and Quality expectations (KPI)
Technology
- Disaster recovery plans
- Information security
- Server and cloud technologies
- Network Management
- Internet of Things
- Utilization and Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- Advanced Inventory Management
- Equipment
- Vehicle Tracking and Operational Efficiency Analys
- Routing and Route Planning
- Process Optimization
- Process Modeling and Simulation
- Autonomous Decision Making Processes
- Operational Monitoring
- Digital Process Flow ( Paperless Process Management )
- Process Analysis and Design
Software
- Warehouse management system
- Transportation management system
- Digital archive management
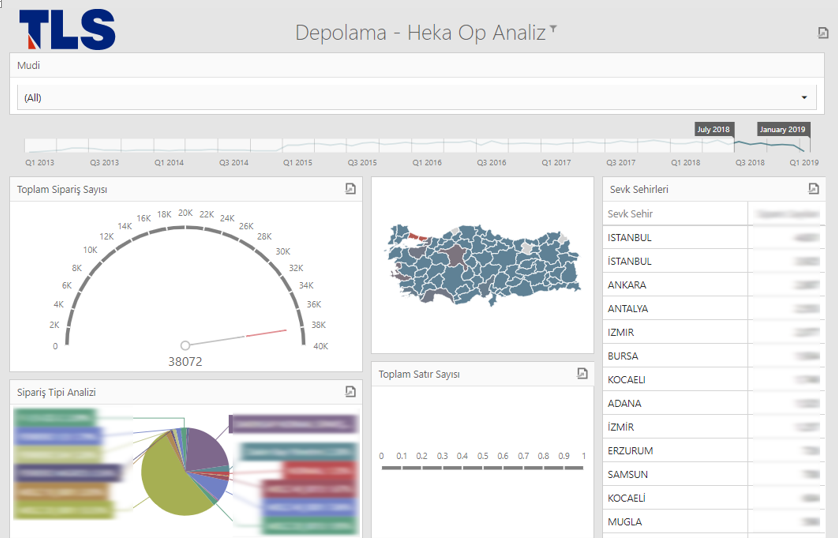
- Big Data analytics
- E-commerce and Omni channel applications
- Integrations (EDI, web service, AS2, FTP protocols).
Robotics and automation
- Robotic warehouse applications
- Artificial intelligence applications
- Safe driving technologies
- Additive technologies
- Predictive maintenance
Quality, Health, and Safety
- Operational Excellence
- Management Systems
- Change Management
- Root Cause Analysis
- Risk Analysis
Process Optimization
Organization and processes in logistics are too complex and too detailed to meet the requirements. Many different parameters like traceability, time, cost, customer service, shelf life stand out in the supply chain processes of various industries like food, pharmaceuticals, machinery, FMCG, electronics, and automotive
Process optimization starts with situation analysis using modern presentation and communication tools of the client and related departments. In addition to the stakeholders responsible for the analysis are subject to a broad stakeholder assessment process, such as information technologies, financial affairs, and customer service. Once the issues for improvement have been analyzed in detail, they are reviewed with simulations as part of the change and risk management process. The optimal value chain is determined through simulations.
Software
The development of easily accessible online portals, the design of user interfaces, and a powerful infrastructure combined with expertise in the functional design of applications provide development opportunities for market-driven and innovative products.
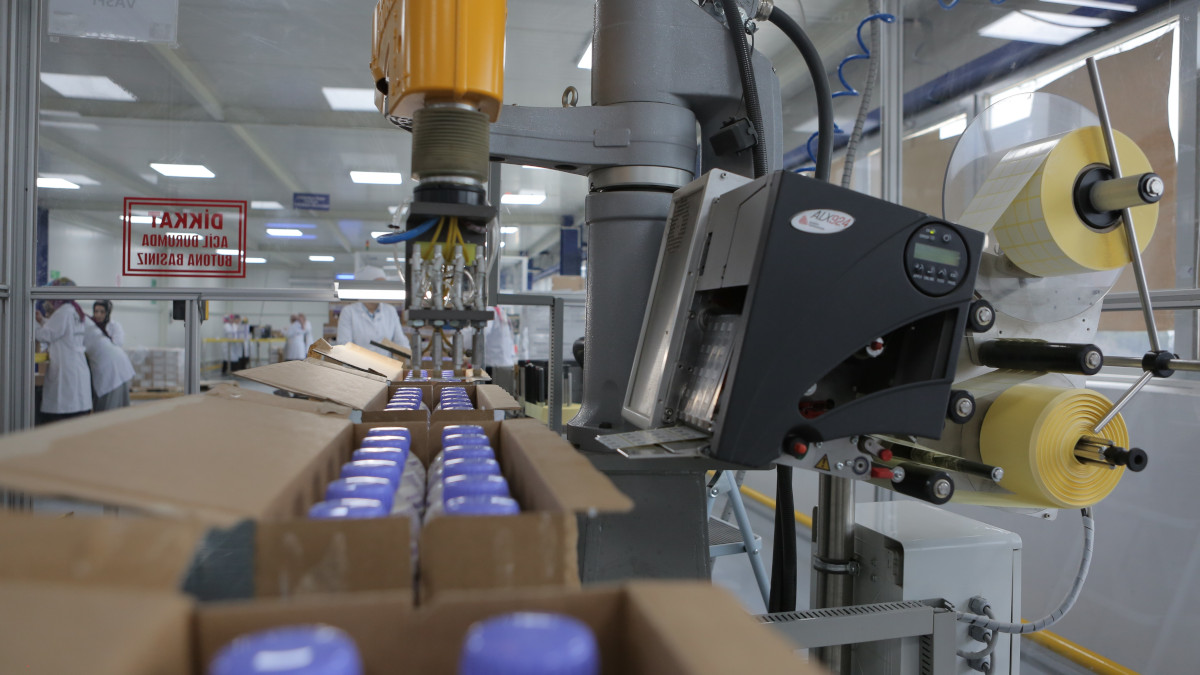
Robotics systems
TLS robotics and automation solutions are indispensable tools for critical supply chain processes. Intelligent and autonomous plants within the concept of Industry 4.0 bring great benefits in terms of decision-making and resource efficiency.
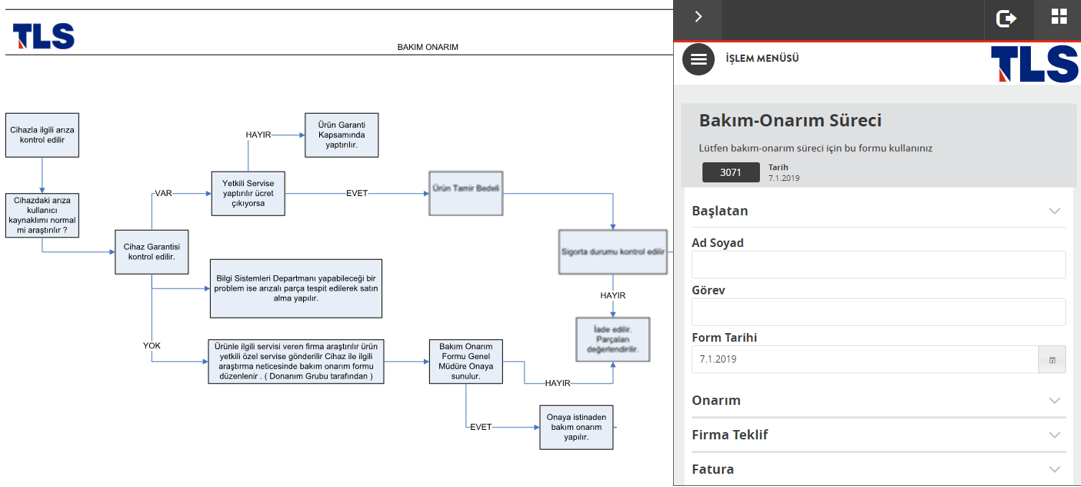
From warehouse automation to Pharmaceutical Track and Trace System (ITS), many operations can be performed by robotics and automation systems in a cost-optimized manner and with high accuracy. In particular, activities such as sorting, labeling, temperature control, and inventory counting work fully integrated with building automation, customer ERP software, regulatory authorities, and process monitoring systems, ensuring continuous online process monitoring and enabling repetitive tasks to be performed with high accuracy and quality.
 |
EDI Integration Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) ensures that the software used in the various supply chain processes and the different types of data are collected in a single portal. The same language is spoken in the processes. With this system, you can track all your incoming and outgoing data such as ERP, planning, warehouse management, accounting, customer relationship management in a single environment, ensuring traceability from production to distribution networks, from suppliers to e-commerce websites. Thanks to this integration, data is transferred accurately and quickly, giving users greater management competence and huge cost advantage. TLS R&D offers a wide range of services that support many different integration infrastructures. It provides end-to-end data transfer via file formats such as XML, Edifact, CSV, TXT, AS2, FTP/SFTP, OFTP, web service, and other communication protocols. |